pleural effusion cat causes
Pleural effusion is a common cause of dyspnea in dogs and cats. Pleural effusion itself is typically fairly easy to treat and the short-term prognosis is usually good.
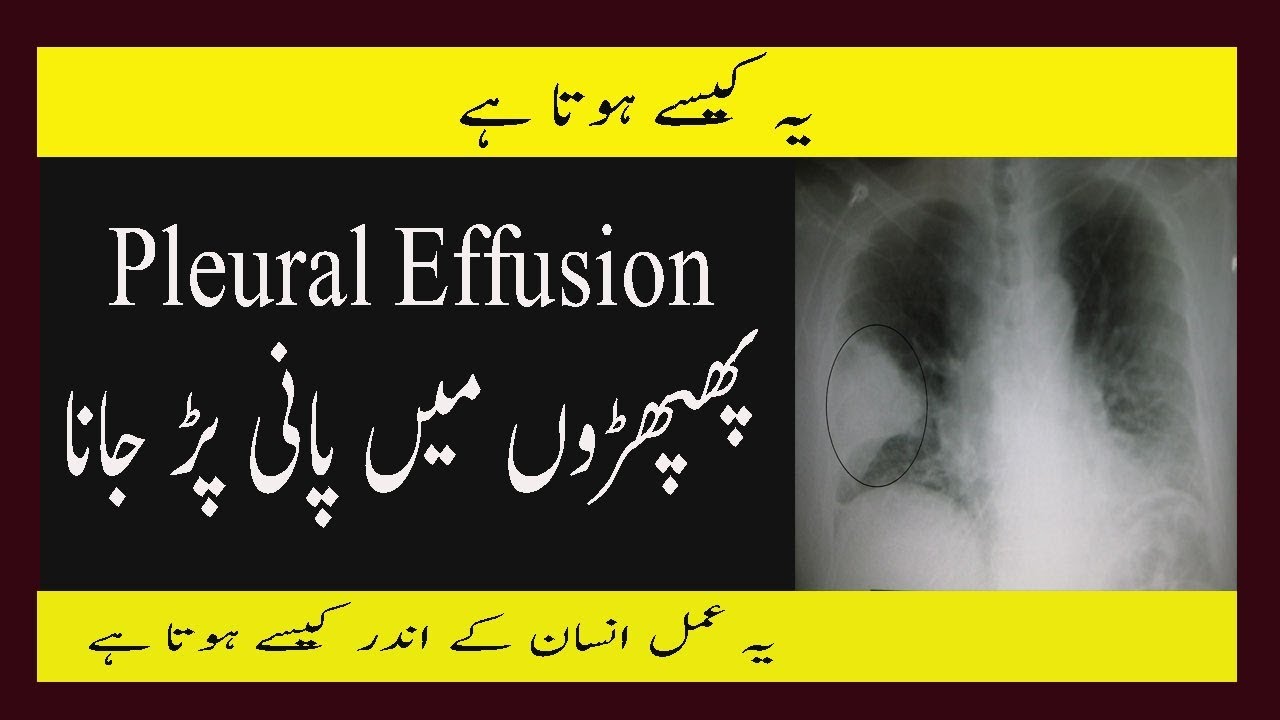
What Is Pleural Effusion Fluid In Lungs And Chest In Urdu Phephron Main Fluid In Lungs Pleural Effusion Lunges
Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma feline infectious peritonitis.

. It is classically an expiratory or mixed dyspnea with absence of normal lung sounds ventrally. J Feline Med Surg. The aetiopathogenic classification of pleural effusion PE can be challenging1 In human medicine PEs are categorised only as transudates resulting from increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased osmotic pressure or exudates resulting from increased vascular permeability2 3 4 5 Simultaneous evaluation of pleural fluid and serum protein lactate.
CD and neoplasia were the most common causes for feline pleural effusion. Pleural effusion is typically. Most cats however will not live more than a year following a diagnosis of lymphoma.
Treatment for feline lymphoma is also usually successful in the short-term with remission rates approaching 75 percent. In a case series of 27 cats the only historical similarity in 56 of the cases was a recent upper respiratory infection. Age liver enzymes as well as cell count protein and glucose levels in the effusion can aid in the investigation of underlying aetiologies.
There are several causes of pleural effusion in dogs and cats. Thymic lymphosarcoma is the most common cause of neoplastic effusions in cats. RESULTS 87 229 cats died or were euthanized before discharge from the hospital.
This term refers to a defect in the diaphragm that allows abdominal organs to. These researchers used medical record data to investigate and characterize potential associations between causes of pleural effusion and clinical signs in cats. The primary conditions that lead to pleural effusion in cats include.
Variables were examined for associations with causes of pleural effusion. Characterizing an effusion by its cytologic properties is an important step in diagnosing the cause of the effusion. What causes pleural effusion.
The most common causes for pleural effusion in all 380 cats were found to be CHF n155 408 and neoplasia n98 258. Variables were examined for associations with causes of pleural effusion. Head trauma can cause pulmonary edema in cats.
Most cases of pleural effusions in cats are due to congestive heart failure CHF neoplasia pyothorax feline infectious peritonitis FIP or idiopathic chylothorax. Cats may develop open-mouthed breathing in an effort to increase air flow. Fluid builds up in the chest either when there is too much of it being produced or when not enough is absorbed or drained by the body.
Pleural effusion is a symptom of many diseases but is rarely a disease itself. Congestive heart failure more common in cats than in dogs Trauma resulting in blood in the thorax called a hemothorax Cancer such as lymphosarcoma adenocarcinoma etc. When FIP affects the chest cavity pleural effusion results.
Excess fluid can accumulate in body cavities from multiple causes. Causes of Pleural Effusion in Cats. What happens if pleural effusion is left untreated.
Diagnostic tests are needed to determine the underlying cause and subsequent treatment recommendations are based on these findings. The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax. Feline infectious peritonitis Feline infectious peritonitis.
This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural space congestive heart failure obstruction of the cranial vena cava the major vein that returns blood to the heart from the front of the body cancer fungal infection feline heartworm. Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort. Congestive heart failure CHF was the most common cause 155 408 of pleural effusion followed by neoplasia 98 258.
Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma FIP nontraumatic diaphragmatic hernia vasculopathy uremic pleuritis hypoproteinemia and vitamin K antagonist toxicity. Bacterial invasion by aerobes and anaerobes eg Streptococcus Staphylococcus Proteus and Pasturella spp and Escherichia coli following puncture of chest wall eg by a bite wound migrating foreign body inflammation Pyothorax. Heart failure Pulmonary embolism Cirrhosis Post open heart surgery.
In dogs and cats the volume of fluid within the peritoneal pleural and pericardial space is quite small generally less than 10ml and fluid cannot. Some affected cats may also cough. These pleural infections are due to para-pneumonic infections from oropharyngeal bacteria.
Resulting in abnormal fluid leaking into the pleural space secondary to a tumor or mass. Neoplastic lymphocytes are usually prolymphocytes or lymphoblasts. Unlike dogs cats with pyothorax can be successfully managed with closed thoracostomy tubes.
RESULTS 87 229 cats died or were euthanized before discharge from the hospital. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes including diseases of the heart lungs or other systemic diseases. Retrospective analysis of pleural effusion in cats.
In some animals a fluid line can be detected where lung sounds are absent ventral to an imaginary horizontal line and increased dorsal to the line. The most common causes of transudative watery fluid pleural effusions include. Depending on its severity and its cause it can lead to a collapsed lung lung scarring or sepsis an out-of-control infection.
Congestive heart failure CHF was the most common cause 155 408 of pleural effusion followed by neoplasia 98 258. Without treatment pleural effusion can be very serious and even life-threatening. Neoplastic effusions may have either a exudative or transudative fluid pattern and are identified by the presence of neoplastic cells on cytological examination.
Below is an overview of pleural effusion in cats followed by in-depth information on the diagnosis and treatment of this condition. In some cats infection with mutated coronavirus can lead to blood vessel damage which results in fluid leakage. Life expectancy of lymphoma without.
Build-up of lymph in the chest chylothorax Cancer.

Fluid In The Chest In Cats Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost Angora Cats Turkish Angora Cat Cat Breeds

Pin By Nonas Arc On Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated Cardiomyopathy Pleural Effusion Heart Muscle

Local Pleural Effusion Medical Knowledge Respiratory Therapy Pleural Effusion

Pin By Great Wolf On Pancreatitis Oedema Acute Pancreatitis Pleural Effusion

Reasons For Heavy Breathing In Cats And How To Help Lovetoknow Heavy Breathing Cat Cat Health Cats

Pleural Effusion In Cats Pleural Sac 2018 01 Pleural Effusion Nursing School Survival School Survival

